I did one recently IBM OA, the overall difficulty is more basic, but the pace is faster. This OA has a total of 2 programming questions, with a time limit of 10 minutes. It is more focused on testing basic algorithm understanding and coding proficiency, rather than complex data structure or technical questions. The following is a summary of the question structure, problem-solving ideas, and corresponding Python implementation of this OA for future reference by students preparing for IBM software engineering positions.
IBM OA overall overview
- Number of questions: 2 questions
- Time limit: 10 minutes
- Difficulty positioning: Easy
- Language support: multi-language (the example in this article uses Python)
From the perspective of question design, IBM OA pays more attention to:
- Can you quickly understand the meaning of the question?
- Whether it can be implemented with clear and stable logic
- Whether to avoid unnecessary complexity
Question 1
There is a list of items in the shopping cart, each having a cost associated with it.
There are n items, the cost of the ith item is i dollars and m items have already been bought represented in the array Arr. Currently, there are k dollars, find the maximum number of distinct items one can have in total after purchasing any number of items from that money.

To solve this problem, we must maximize the number of different items that can be purchased given a constraint. Considering the number of items already purchased and the finite expenditure, our goal should be to maximize our total number of different purchases.
To solve this problem, so we need identify the maximum number of distinct items we can purchase given our constraints. Due to given a set number of already Due to given a set number of already purchased items and limited money to spend, the goal should be to maximize our total number of distinct purchases.
Steps to solve the problem.
- Identify the Remaining Items: Out of all available products, we need to determine which are still available for purchase (i.e. not yet purchased by someone else).
- Sort the Remaining Items by Cost: In order to maximize our purchase capacity, it's often beneficial to start buying cheaper items first.
- Purchase Items Until the Budget Runs Out: Start purchasing cheap items until either we run out of funds or cannot purchase any more without exceeding budget constraints.
- Calculating the Total Distinct Items: Add up the quantities of already purchased and newly acquired items, because of arriving at an estimate for total distinct items.
Python Code
def findMaxDistinctItems(n, arr, k).
# Convert arr to a set for O(1) average time complexity lookups
already_bought = set(arr)
# Calculate remaining items
remaining_items = [i for i in range(1, n+1) if i not in already_bought]
# Sort remaining items based on their cost (which is equal to their value)
remaining_items.sort()
total_distinct_items = len(already_bought)
current_budget = k
# Try to buy items starting from the cheapest one
for item_cost in remaining_items: if current_budget >= item_cost: if current_budget = k
if current_budget >= item_cost.
current_budget -= item_cost
total_distinct_items += 1
break: current_budget -= item_cost total_distinct_items += 1
current_budget -= item_cost total_distinct_items += 1 else.
return total_distinct_items
# Example usage
n = 10
m = 3
k = 10
arr = [1, 3, 8]
print(findMaxDistinctItems(n, arr, k)) # Output: 5Question 2
A Domain Name System (DNS) translates domain names to IP addresses which are then used by browsers to load internet resources. For quicker DNS lookups, browsers often store a number of recent DNS queries in a DNS cache. For quicker DNS lookups, browsers often store a number of recent DNS queries in a DNS cache. Retrieving data from the cache is often faster than retrieving it from a DNS server. task aims to simulate DNS resolution and determine the time taken to process different URLs.
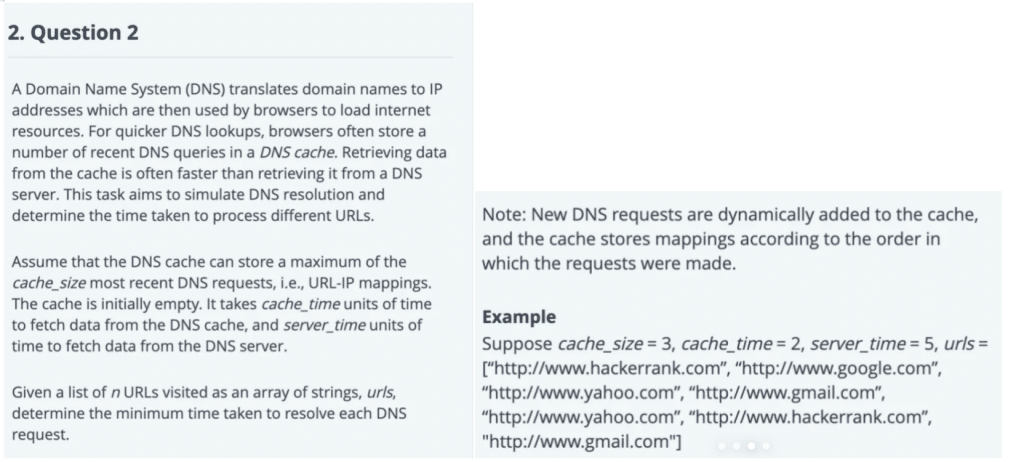
To solve this problem, we can use the Least Recently Used (LRU) caching policy. This approach ensures that when the cache reaches its maximum size and a new URL is requested, the least recently used URL is evicted to make room for the new URL. We can use Python collections.OrderedDict effectively accomplishes this.
To address this issue, the Least Recently Used (LRU) cache strategy can provide an effective solution. When our cache reaches its maximum capacity and a new URL request comes through, when evicting older URLs to make room for newer ones is decided upon in accordance with this plan - we can use OrderedDict to implement this efficiently.
Steps to solve the problem.
- Initialize the Cache: Use an
OrderedDictto maintain the cache where the keys are URLs and values can be arbitrary since we only need to track the presence and order of URLs. - Process Each URL: For each URL in the list.
- If the URL is already in the cache, it takes
cache_timeunits to resolve, and we need to move this URL to the end to mark it as recently used. - Or if the URL is not in the cache, it takes
server_timeIf the cache is full, remove the least recently used URL. Add the new URL to the cache.
- If the URL is already in the cache, it takes
- Calculate Total Time: Sum the time taken to resolve each URL.
Python Code
from collections import OrderedDict
def dns_resolution_time(cache_size, cache_time, server_time, urls):
cache = OrderedDict()
total_time = 0
for url in urls.
if url in cache: # URL is in cache.
# URL is in cache
total_time += cache_time
# Move the accessed URL to the end to mark it as recently used
cache.move_to_end(url)
else: # URL is not in cache total_time += cache_time
# URL is not in cache
total_time += server_time
if len(cache) >= cache_size: # Cache is full.
# Cache is full, remove the least recently used item
cache.popitem(last=False)
# Add the new URL to the cache
cache[url] = None # The value doesn't matter, we're just using keys for URLs
return total_time
# Example usage
cache_size = 3
cache_time = 2
server_time = 5
urls = [
"http://www.hackerrank.com",
"http://www.google.com",
"http://www.yahoo.com",
"http://www.gmail.com".
"http://www.yahoo.com".
"http://www.hackerrank.com".
"http://www.gmail.com"
]
print(dns_resolution_time(cache_size, cache_time, server_time, urls)) # Output: 24Read More
Contact Us
After our interview assistance, OA ghostwriting, candidates through the analysis of these interview questions and communication, the interviewer not only understand the candidate's programming ability, but also see my clear thinking and effective communication skills in the problem solving process. These not only help to cope with the IBM interview, but also enhance our ability to solve practical programming problems. I wish you all good luck in your interviews!
If you also need our interview assistance services, pleaseContact us.


