最近做了一场 IBM OA ,整体难度偏基础,但节奏较快。本次 OA 共 2 道编程题,限时 10 分钟,更偏向对基础算法理解与代码熟练度的考察,而不是复杂的数据结构或技巧题。下面整理本次 OA 的题目结构、解题思路以及对应的 Python 实现,供后续准备 IBM 软件工程类岗位的同学参考。
IBM OA 整体概览
- 题目数量:2 题
- 时间限制:10 分钟
- 难度定位:Easy
- 语言支持:多语言(本文示例使用 Python)
从题型设计来看,IBM OA 更关注:
- 是否能快速读懂题意
- 是否能用清晰、稳定的逻辑完成实现
- 是否避免不必要的复杂度
Question 1
There is a list of items in the shopping cart, each having a cost associated with it.
There are n items, the cost of the ith item is i dollars and m items have already been bought represented in the array arr. Currently, there are k dollars, find the maximum number of distinct items one can have in total after purchasing any number of items from that money.

为了解决这个问题,我们必须在给定约束的情况下可以购买的不同物品的最大数量。考虑到已经购买的物品数量和有限的支出,我们的目标应该是最大限度地增加我们的不同购买总数。
To solve this problem, so we need identify the maximum number of distinct items we can purchase given our constraints. Due to given a set number of already purchased items and limited money to spend, the goal should be to maximize our total number of distinct purchases.
Steps to solve the problem:
- Identify the Remaining Items: Out of all available products, we need to determine which are still available for purchase (i.e. not yet purchased by someone else).
- Sort the Remaining Items by Cost: In order to maximize our purchase capacity, it’s often beneficial to start buying cheaper items first.
- Purchase Items Until the Budget Runs Out: Start purchasing cheap items until either we run out of funds or cannot purchase any more without exceeding budget constraints.
- Calculating the Total Distinct Items: Add up the quantities of already purchased and newly acquired items, because of arriving at an estimate for total distinct items.
Python Code
def findMaxDistinctItems(n, arr, k):
# Convert arr to a set for O(1) average time complexity lookups
already_bought = set(arr)
# Calculate remaining items
remaining_items = [i for i in range(1, n+1) if i not in already_bought]
# Sort remaining items based on their cost (which is equal to their value)
remaining_items.sort()
total_distinct_items = len(already_bought)
current_budget = k
# Try to buy items starting from the cheapest one
for item_cost in remaining_items:
if current_budget >= item_cost:
current_budget -= item_cost
total_distinct_items += 1
else:
break
return total_distinct_items
# Example usage
n = 10
m = 3
k = 10
arr = [1, 3, 8]
print(findMaxDistinctItems(n, arr, k)) # Output: 5Question 2
A Domain Name System (DNS) translates domain names to IP addresses which are then used by browsers to load internet resources. For quicker DNS lookups, browsers often store a number of recent DNS queries in a DNS cache. Retrieving data from the cache is often faster than retrieving it from a DNS server. This task aims to simulate DNS resolution and determine the time taken to process different URLs.
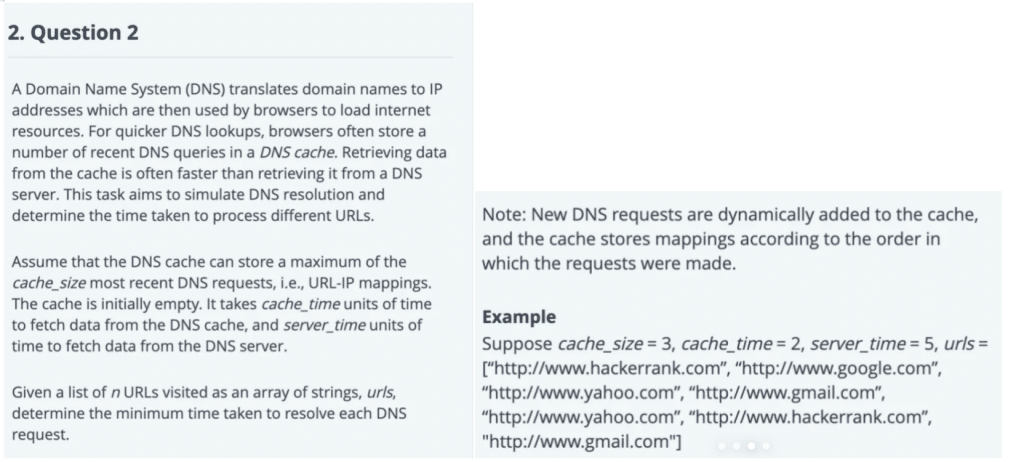
为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用最近最少使用(LRU)缓存策略。这种方法确保了当缓存达到其最大大小,并请求新的URL时,会驱逐最近使用最少的URL,为新URL腾出空间。我们可以使用Python的集合。OrderedDict有效地实现了这一点。
To address this issue, the Least Recently Used (LRU) cache strategy can provide an effective solution. When our cache reaches its maximum capacity and a new URL request comes through, when evicting older URLs to make room for newer ones is decided upon in accordance with this plan – we can use Python collections.OrderedDict to implement this efficiently.
Steps to solve the problem:
- Initialize the Cache: Use an
OrderedDictto maintain the cache where the keys are URLs and values can be arbitrary since we only need to track the presence and order of URLs. - Process Each URL: For each URL in the list:
- If the URL is already in the cache, it takes
cache_timeunits to resolve, and we need to move this URL to the end to mark it as recently used. - Or if the URL is not in the cache, it takes
server_timeunits to resolve. If the cache is full, remove the least recently used URL. Add the new URL to the cache.
- If the URL is already in the cache, it takes
- Calculate Total Time: Sum the time taken to resolve each URL.
Python Code
from collections import OrderedDict
def dns_resolution_time(cache_size, cache_time, server_time, urls):
cache = OrderedDict()
total_time = 0
for url in urls:
if url in cache:
# URL is in cache
total_time += cache_time
# Move the accessed URL to the end to mark it as recently used
cache.move_to_end(url)
else:
# URL is not in cache
total_time += server_time
if len(cache) >= cache_size:
# Cache is full, remove the least recently used item
cache.popitem(last=False)
# Add the new URL to the cache
cache[url] = None # The value doesn't matter, we're just using keys for URLs
return total_time
# Example usage
cache_size = 3
cache_time = 2
server_time = 5
urls = [
"http://www.hackerrank.com",
"http://www.google.com",
"http://www.yahoo.com",
"http://www.gmail.com",
"http://www.yahoo.com",
"http://www.hackerrank.com",
"http://www.gmail.com"
]
print(dns_resolution_time(cache_size, cache_time, server_time, urls)) # Output: 24Read More
Contact Us
经过我们的面试辅助,OA代写,候选人通过这些面试题的解析和沟通,面试官不仅了解了候选人的编程能力,也看到了我在解决问题过程中清晰的思路和有效的沟通技巧。这些不仅有助于应对IBM的面试,同时也能提升我们解决实际编程问题的能力。祝大家面试顺利!
如果你也需要我们的面试辅助服务,请联系我们。


