Weride 這三年在穩步發展,是自動駕駛領域的頭部企業之一。 融資和商業化情況非常不錯,已經進入 pre-IPO 階段。 目前在中國、 美國、新加坡都有分部。 國總部位於 San Jose, 工作環境良好,同事優秀,提供免費午餐晚餐,有許多機會回國出差。 今年也擴大了 NG 和 intern 的規模,目前還有大量的 HC。 現在的大環境對於 NG/Intern 來說比較困難,所以來給大家撐傘啦。 這篇文章分享一些我們親身總結的 weride oa 面經。

Weride OA Question 1: Distance Metric
For each element in a given array, calculate the absolute value of index differences between it and all other elements of the same value. Return theresulting values in an array.
For example, if the array elements at indices 2 and 3 are equal, the distance metric for element 2 is ∣3−2∣=1|3 – 2| = 1. Forelement 3 it is ∣3−2∣=1|3 – 2| = 1.
Example:
Input:
n = 6
arr = [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 3]The element arr[0] = 1. Similar elements are at indices 2 and 4.
Distance metric for arr[0]: ∣0−2∣+∣0−4∣=5|0 – 2| + |0 – 4| = 5.
Solve question:
Distance metric for each element:
- The distance metric for
arr[0] = 1: ∣0−2∣+∣0−4∣=5. - The distance metric for
arr[1] = 2: ∣1−3∣=2. - The distance metric for
arr[2] = 1: ∣2−0∣+∣2−4∣=4. - The distance metric for
arr[3] = 2: ∣3−1∣=2. - The distance metric for
arr[4] = 1: ∣4−0∣+∣4−2∣=6. - The distance metric for
arr[5] = 3: No other similar elements. Distance = 0.
Resulting distance metrics: [5, 2, 4, 2, 6, 0].
Function Description
Complete the function getDistanceMetrics in the editor below.
Function Signature
def getDistanceMetrics(arr: List[int]) -> List[int]:Parameters
arr(List[int]): An array of integers.
Returns
List[int]: An array of integers representing the sum of the distance metrics for each element inarr.
Weride OA Question 2: Bob Navigates a Maze
Bob and Alice have teamed up on a game show. After winning the first round, they now have access to a maze with hidden gold. If Bob can collect all the gold coinsand deliver them to Alice’s position, they can split the gold. Bob can move horizontally or vertically as long as he stays within the maze, andthe cell is not blocked.
The maze is represented by an n×m grid, where each cell has a value:
- 0: Open cell
- 1: Blocked cell
- 2: Open cell containing a gold coin
Bob starts at the top-left corner of the maze at cell (0,0), and Alice’s position is given by (x,y). Determine the shortest path Bob can follow to:
- Collect all the gold coins in the maze.
- Deliver the coins to Alice at (x,y).
If it is impossible for Bob to collect all the gold coins or deliver them to Alice, return -1.
Example: maze = [[1,0,2],[1,2,0],[1,0,0]] with Alice at (2,2).
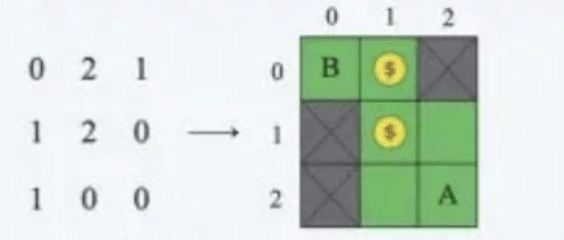
B represents Bob’s starting position at (0,0), and A represents Alice’s position (which will also be Bob’sfinal position). As Bob starts at (0,0), he has two possible paths to collect the gold coins and deliver them to Alice:
- (0,0)→(0,1)→(1,1)→(2,1)→(2,2)
- (0,0)→(0,1)→(1,1)→(1,2)→(2,2)
Both paths have a length of 4 and represent the shortest path.
Function Description
Complete the function minMoves in the editor below. The function must return the integer length of Bob’s shortest path to collect all gold coins and deliver them to Alice, or -1 if it is not possible.
Function Signature
def minMoves(maze: List[List[int]], x: int, y: int) -> int:
# Your implementation hereParameters
maze: A 2D array of integers representing the maze.x: An integer denoting Alice’s row coordinate.y: An integer denoting Alice’s column coordinate.
Approach
- Record the positions of all the gold coins and use a binary representation to track the collection state of each coin.
- Use Breadth-First Search (BFS) starting from the initial position (0,0). At each step, track the current position, the state of collected coins, and the current step count.
- For each position, try moving in four directions (up, down, left, right). Update the state of collected coins and mark visited states.
- If Bob reaches Alice’s position and has collected all the gold coins, return the current step count. Otherwise, continue the search.
- If the search completes without meeting the conditions, return
-1.
Weride OA Question 3: Discount Events
A general store at Hackerland sells n items with the price of the i-th item represented by price[i]. The store adjusts the prices of items based on inflation as queries of two types:
1 x v: Change the price of thex-th item tov.2 v: Change any price that is less thanvtov.
Given an array price of n integers and the price adjustment queries, return the final prices of all items.
Example
Input:
n = 3 price = [7, 5, 4] q = 3 queries = [[2, 6, 0], [1, 2, 9], [2, 8, 0]]
Explanation of queries:
[2, 6, 0]: Change elements less than 6 to 6. Nowprice = [7, 6, 6].[1, 2, 9]: Change the 2-nd element to 9. Nowprice = [7, 9, 6].[2, 8, 0]: Change elements less than 8 to 8. Nowprice = [8, 9, 8].
Output:
[8, 9, 8]Function Description
Complete the function getFinalPrice in the editor below.
Function Signature
def getFinalPrice(price: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:Parameters
price(List[int]): An array of integers representing the prices of items.queries(List[List[int]]): A 2D array where each query is represented as a list of integers.
Returns
List[int]: The final array of prices after all queries are executed.
參考資料
We provide services for writing online assessments (OA), proxy interviews, and interview assistance. For the OA writing service, we will ensure that youachieve a perfect score. 聯絡我們 現在預約。

